
Shutdown Maintenance:
Plan, Execute, Optimize
Table of Contents
ToggleShutdown Maintenance Process
What is Shutdown Maintenance?
Shutdown maintenance refers to the temporary closure of a plant or section of a plant, to carry out planned preventive maintenance activities of all the equipment therein. Isolated preventive maintenance of equipment is not feasible in continuous process industries and preventive inspections, improvements and spare replacements require the plant operations to be stopped, requiring shutdown maintenance. Shutdown maintenance involves many moving parts, usually lasts for a number of days or weeks, and hence is planned well in advance.
Shutdown maintenance is also referred to variously as maintenance shutdowns, maintenance turnarounds, turnarounds (TAr), Turnaround Maintenance (TAM) or Turnaround, Shutdowns and Outages (TSO). Shutdown maintenance is costly, time-consuming, and with high risks but is an essential and critical element of plant maintenance strategy. Shutdown maintenance is an essential and integral element of plant lifecycle in process industries and other industries having continuous operations. Some industries invoke seasonal shutdowns and turnovers based on environmental factors (eg. Hydropower plant shutdown based on river flow/winter freeze)
How does Shutdown Maintenance differ from Regular Preventive Maintenance?
Shutdown maintenance is a planned preventive maintenance activity. However, it differs from regular preventive maintenance in the following ways
- Stoppage of entire plant operations or a section thereof
- The scale and extent of work executed is huge
- Multiple maintenance work orders are being executed simultaneously and at times in specific sequence with interdependencies
- Longer duration of time over which maintenance activities are carried out
- Higher risk of the shutdown maintenance due to its complexity and criticality to business operations as compared to regular preventive maintenance activity
Shutdown maintenance is often confused with plant outage or maintenance outage. Though plant operations are stopped in both of these events, they are different. Plant outages can be caused by any of unplanned events eg. equipment breakdowns, power outages, service disruptions or raw material shortages. Shutdown maintenance or turnaround is a planned and scheduled event and thus differs from plant outage or maintenance outage which is a forced event.
Scope of Shutdown Maintenance
The scope of Shutdown Maintenance varies based on industry and operating schedule. The shutdown process and scope will be more complex for plants operating 24×7 (eg. Power plants, Oil refineries), than those plants that are operating in shifts. Scope of shutdown maintenance includes
- Maintenance backlog set aside for shutdown maintenance
- Proactive equipment inspections to identify latent issues (eg. Boilers and Pressure vessels)
- Inspection, cleaning and repair of utilities, Pipelines, storage tanks etc.
- Corrective maintenance of prior known failures and performance deteriorations
- Planned preventive maintenance activities and improvements identified via predictive maintenance (PdM)
- Management of change activities including Replacement or overhaul of equipment, faulty sections, components and/or sub-assemblies, retrofit of pollution control or energy-saving equipment
- Streamlining of certain plant operations and efficiency improvements
- Unplanned work uncovered during shutdown maintenance (eg. Corrosion)
- Equipment safety and reliability improvements
Benefits of Shutdown Maintenance
Shutdown Maintenance is focused on improving plant operations and efficiency. Benefits of planned shutdown maintenance include
- Downtime Reduction: When executed effectively, Shutdown Maintenance can improve the availability and uptime of individual equipment, thereby increasing the overall plant availability, throughput and Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE).
- Increase in Operational Efficiency: Plant efficiency improves significantly as bottlenecks, performance degradations and deficiencies have been addressed. Increased performance of individual equipment means lower energy costs, and overall improvement of plant efficiency and operations.
- Increase in Reliability: Shutdown maintenance has a strong emphasis on improving equipment efficiency and plant performance. Avoidance of plant outages and equipment failures improves equipment reliability and plant reliability.
- People Productivity: Productivity of the production and maintenance team increases, since they are spending less time on plant outages and equipment failures and more time on productive activities. Increased productivity improves the business goals and generates more output per employee
- Enhanced Asset Life: Shutdown maintenance brings in a structured approach to planned preventive maintenance that is executed on the related equipment in a systematic and structured manner. It not only improves the equipment performance but also its useful life. Thus it extends asset life and avoids high equipment replacement costs.
- Safety and Sustainability of Operations: Since the plant has better equipment and performance, it provides a safe workplace for people. Efficiency improvements reduce waste and effluents, thereby promoting a safe environment and sustainability of operations.
- Improves Return on investment: Increase in asset availability and equipment reliability improves the plant performance, utilization and throughput. Deficiency resolution ensures loss avoidance, energy savings, better production output and waste reduction. All of these contribute directly to revenue, return on investment and plant profitability.
Shutdown Maintenance Procedure
The shutdown of a plant is costly. Each day of plant outage impacts production and results in revenue loss. The shutdown maintenance cycle has to be short, focused and efficient to bring out the planned operational efficiencies. Shutdown maintenance requires extensive preparatory work, budgetary approvals, project planning and execution, delivery of multiple sub-projects in a coordinated way, managing people, process and systems, progress monitoring and course corrections and closeout.
Regular preventive maintenance or breakdown maintenance involves work order execution for one piece of equipment at a time or at best a few pieces of equipment. And the duration of the work order for such preventive or breakdown maintenance will be no more than a few days. Shutdown maintenance is a lot similar to a project or program, wherein many work orders and maintenance activities need to be executed simultaneously or in a specified sequence with clear dependencies on each other. Thus shutdown maintenance is a lot more complex than regular breakdown maintenance or preventive maintenance activities
Efficient Shutdown Maintenance involves the following five phases
Preparatory Work & Scoping:
- Preparatory work involves collating all the maintenance work that needs to be performed during shutdown maintenance, based on past shutdowns and including improvements identified during inspections and regular operations.
- Scoping the work and deliverables including a list of equipment to be brought down and the maintenance activities to be performed,
- Estimation of cost, time, efforts and supporting resources (people, contract labour, vendors, tools) required and preparation of the budgetary plan
- Project organization to plan, lead and execute the Shutdown maintenance. Identification of the key stakeholders, shutdown team members and their roles and responsibilities
- Timing of the shutdown cycle, including the shutdown start date and shutdown duration, coordinating with business stakeholders to manage production loss
- Documenting the isolation / re-energization procedures, safety processes and sustainability initiatives
- Identification of training needs for the shutdown team members and ensuring appropriate training including safety aspects
- Finalizing the shutdown maintenance project objectives including scope, cost (budget), time, milestones, efforts, safety, risk and recovery plans
- Securing necessary management approvals for the Shutdown project – objectives, plan, duration, budget and project team
Project Planning & Scheduling:
Project planning is a critical task that details the sub-projects, prioritizations and project sequencing of dependencies and critical path management, estimation of durations and scheduling them, identifying resources required (man, machine, supporting tools like a crane, spares for replacement), permits and process approvals required, project organization and communications, setting up support systems, risk management procedures etc.
The shutdown maintenance planning organization will comprise cross-functional team members with expertise across different plant units and their operations, project managers, shutdown planners and shutdown coordinators. A shutdown Project is normally led by a senior plant leader, who has insights into plant operations and prior experience in past shutdowns. Based on the scope of the project, he/she will be assisted by one or more Project Managers.
Experienced planners outline the plan with a detailed work breakdown structure and job plans with task level staffing and estimation, taking into account past shutdown histories, safety, risk and project management principles. Equipment under warranty and Annual Maintenance contracts may require vendor coordination. External approvals, from regulatory bodies or governmental agencies or local communities, if any, that are needed for shutdown shall also be planned. A detailed list of spare inventory required for the shutdown maintenance will be prepared and the relevant spares procured and kept in readiness. Site logistics including Tools (eg. Forklifts, Cranes) procurement, either from in-house or from rental companies, need to be planned in advance. The master list of shutdown maintenance activities and job plans needs to be constantly updated with newer discoveries and additional work that needs to be done.
Shutdown coordinators will interface with the operational team during the execution phase and coordinate all the bi-directional needs between the planning and execution team.
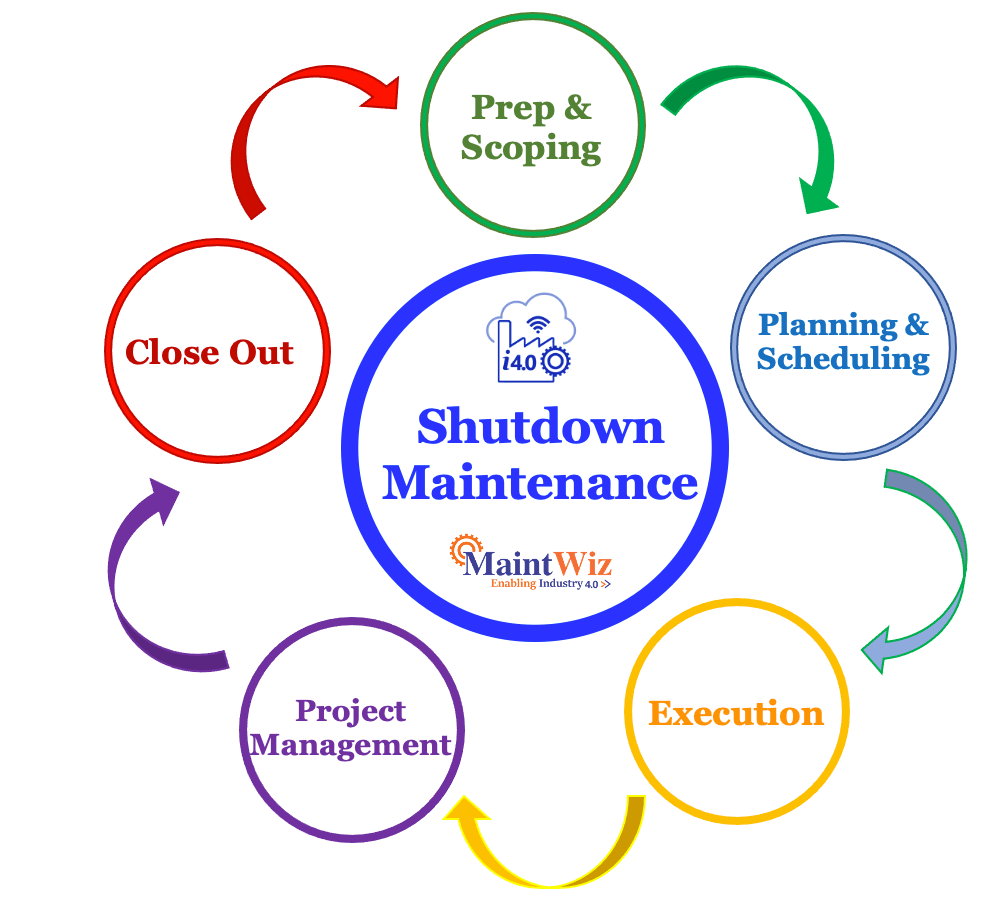
Project Execution
- Mobilization of teams, receipt of material(Spares, PPE, Consumables), tools and other resources. Organizing safety and other training and preparatory activities
- Securing necessary safety approvals and work permits, risk identifications, clearances, performing lock out tag out (LOTO) procedures, isolation and de-energization
- Shutting down the plant operations completely in a pre-planned sequence
- Inspections of equipment, utilities, pipelines, heat transfer systems, reactors etc. to assess condition, fitness and reliability. Safety assessments of the equipment, where required
- Cleaning the pipelines, storage tanks etc. and disposal of waste and effluents
- Preventive Maintenance tasks to be carried out for the various equipment and assets as per the defined plan and checklists, replacement of spares
- Equipment replacements, disassembly of equipment to carry out maintenance and reassembly, Repairs and refurbishments of identified pipeline sections, break-fix of damages and malfunctions identified during inspections
- Instruments recalibrations needed to meet compliance requirements
- Evaluation of individual equipment and readiness assessment, quality assurance and control
- Evaluation and prioritization of unplanned maintenance work uncovered during the execution phase of shutdown maintenance. Integration of such unplanned maintenance work with the master project plan
- Starting back of the plant in the pre-defined sequence. The most critical activity is to ensure the plant operations are restored and production is resumed. Any delay herein will cause a huge financial loss.
Project Management
- Overall progress tracking against the baseline activities and milestones defined, and successful completion of maintenance tasks that need to be executed in each activity
- Monitoring the critical path of project activities, pre-requisites and sequels
- Project communications including stakeholder communications. Includes periodic communications and publications of status and metrics, bottom-up communications from the shutdown execution team to management, top-down communications from management and horizontal communication between team members and different teams. Project communication is very vital and dedicated team members will coordinate the collection and publication of project metrics, process communications, notifications and instructions etc.
- Budget and schedule variances monitoring
- Internal and external co-ordinations. Internal coordination is required with project managers and coordinators, planners, material managers, safety officers and other execution teams. External coordination, with vendors, specialized service providers, inspection agencies, regulatory authorities (eg. Pollution, Industrial Safety agencies), certification authorities etc. may be required depending on the nature and scope of the shutdown project
- Managing unscheduled changes
- Risk management and improvements
Close Out
- Demobilization of execution teams, discharging contract staff, return of tools, vendor sign-off, disposal of all excess materials, permits and approvals close out etc.
- Account closures, budget review and variances tracking
- Review of the shutdown to start-up activities, project performance, major tasks completion, what went wrong, cost and schedule variances, KPIs / metrics, safety / EHS practices and tracking of results and efficiency improvements
- Documentation of the opportunities for improvement, best practices and learnings for future shutdown maintenance projects
- Preparation and submission of reports to Senior Management
Shutdown projects are huge and complex with many inter-linkages. It can be overwhelming for any team to handle. Staffing with the right resources with deep domain knowledge in plant operations and equipment, and project management experience can help navigate this challenging task efficiently. Turnaround Maintenance (shutdown) has become a specialized and expert-driven practice and today experienced professional organizations offer sector-specific TSO services to deliver it as a packaged project.
What are the technology tools that can help in Shutdown Maintenance?
Enabling IT systems like Project Management tools can improve Shutdown maintenance through project functionalities like critical path, project scheduling, progress tracking and budget variance. Modern Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS or CMMS Software) have a lot of these functionalities built in as well and can provide triple benefits – comprehensive equipment maintenance functionality, robust project management capability and an integrated view of asset management/plant maintenance history.
How can MaintWiz Industry 4.0 CMMS Software Help You in Your Shutdown Maintenance?
The success of shutdown management requires a combination of robust processes, a talented team and enabling technology. CMMS Software can unify the man, machine process interactions to deliver an integrated solution that can meet the business objectives of plant shutdown.
MaintWiz is a comprehensive Industry 4.0 CMMS that provides all the functionalities need to build a robust Shutdown Maintenance program. It provides a complete platform for planning, organizing, staffing, executing and managing your Shutdown projects in the most efficient and cost-effective manner.
Principal features include
- Full asset register that can include all the plant equipment list and sub-assemblies, criticality, past failures and past asset history
- Exhaustive tool set for scoping the shutdown project and creating and managing individual work orders, through their life cycle. MaintWiz industry 4.0 CMMS software supports project management functionalities for shutdown project planning and efficient execution of the individual maintenance work orders.
- Comprehensive functionalities to address Budgeting, Permits and Approvals, Spares Inventory Planning, Vendor Management and Project Team Communications
- Custom dashboards and interactive charts that can provide insights on project progress and status, budget and schedule variances, maintenance metrics, people productivity and forecasts.
- Supports standardized processes and repeatable operations. Helps consistent performance, and institutionalizes learnings and improvements.
- MaintWiz features Easy use interfaces that improve user adoption and engagement. Calendar views to show visual depictions. Mobile maintenance app to complete work at the point of work.
Request a one-one demo with our solution engineering team.

Request a one-one demo with our solution engineering team.




