
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Preventive Maintenance
Preventive maintenance (sometimes referred to as preventative maintenance) is a critical component of asset management and plant maintenance strategy. Preventive maintenance involves planned inspections, routine maintenance activities, cleaning and lubrication and proactive replacement of worn-out and end-of-life spares, to avoid catastrophic failures. Planning and completing maintenance tasks proactively and on time, helps minimize outages and extends equipment life. It avoids costly unplanned downtime and improves asset availability, safety, performance and utilization.
Preventive Maintenance can be scheduled based on elapsed calendar time (time-based maintenance), equipment usage (eg. Run hours/production output – usage-based maintenance), and performance of critical parameters (eg. Vibration – condition-based maintenance) or event-based maintenance.
What is Preventive Maintenance Program?
To ensure the success of a preventive maintenance program, it’s essential to incorporate condition monitoring techniques. Condition monitoring involves regularly assessing the health and performance of equipment, which allows maintenance teams to detect potential issues before they become critical. By using tools such as vibration analysis, oil analysis, and thermal imaging, maintenance teams can identify abnormal patterns or signs of wear and tear and take corrective action before the equipment fails. This proactive approach to maintenance not only reduces downtime but also extends the lifespan of equipment, ultimately improving the overall effectiveness of the preventive maintenance program.
A preventive maintenance plan of individual equipment focuses on improving the availability of that specific equipment. Plants have many assembly lines, wherein a set of equipment needs to run together to avoid plant/section/line downtime and maximize production output. The breakdown of a single machine can stop production. Preventive Maintenance programs look at the entire set of equipment and their preventive maintenance plans in a holistic and integrated manner to achieve operational efficiency.
Preventive Maintenance programs bring a structured and systematic approach to planning and execution of all the plant/line preventive maintenance activities together and in a more efficient and cost-effective manner. Systems, processes and tools help in managing the complexity and making it simpler and easy to administer. Preventive Maintenance programs are useful in plant and machinery maintenance, facility management and building maintenance, utility maintenance, fleet maintenance, infrastructure maintenance, aviation maintenance etc.
Components of Preventive Maintenance Program
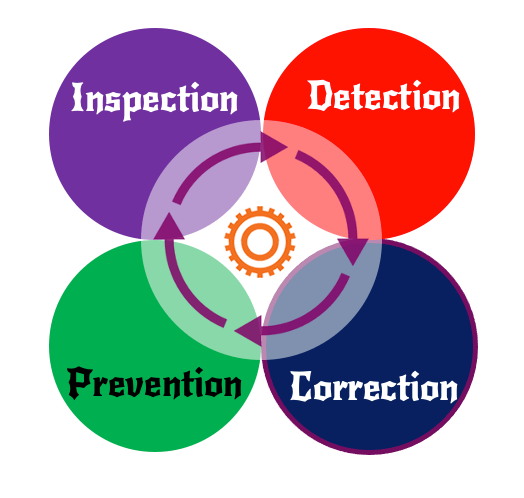
Preventive Maintenance programs have 4 critical components
- Inspection: Regular plant equipment inspections ensure that the equipment is performing efficiently and are safe-to-use. Inspections can identify maintenance activities that need to be executed, spare parts replacement, non-conformances and deviations, safety issues and performance issues.
- Detection: Preventive Maintenance programs help plant maintenance teams to detect problems early, based on symptoms and early warning signs. Early detection helps in quick interventions before complete equipment failure, better planning and resolution of issues without impacting production line output.
- Correction: Inspections and early detections can help fix the issues before they become catastrophic. Timely corrections, repairs and spare part replacements can improve equipment performance and avoid unscheduled downtime.
- Prevention: Routine cleaning, lubrication, inspection, tightening and adjustment activities (CLITA activities) ensure equipment performance is in line with the manufacturer’s specifications and avoids failures.
Benefits of Preventive Maintenance Program
- Preventive Maintenance programs ensures the entire set of plant assets work at full efficiency
- Preventive Maintenance programs reduces costly failures and performance deteriorations of individual equipment and thus ensures maximum production output and avoids revenue loss
- Since the plant assets work at higher efficiency, energy usage is optimized and saves operational costs
- Improves the safety of the people, equipment and work environment.
- Preventive Maintenance programs are planned interventions. Thus preventive maintenance can be done together for the equipment working together, thus improving their collective availability and operational efficiency.
- Down time during line stoppage can be utilized to advance planned preventive maintenance tasks for the upstream and downstream equipment, thereby increasing uptime.
- Preventive Maintenance programs look holistically and thus maximize overall plant operations while optimizing maintenance cost, effort and time.
- Preventive Maintenance programs extends the life of plant assets, their performance and utilization thereby maximizing return on investments.
How to set up Effective Preventive Maintenance Programs
Goals and Objectives:
Like any organizational initiative, aligning the objectives of the Preventive Maintenance program with that the business goals is mandatory. Preventive Maintenance programs that are derived from plant-level asset goals can easily secure budget, resources and management bandwidth to ensure successful delivery.
Preventive Maintenance program goals can be set for equipment availability, plant downtime, frequency and repetition of failures, equipment performance, cost of maintenance etc. The expected benefits of a preventive maintenance program can be optimally realized. Many plants have some kind of preventive maintenance program in place but fail to achieve expected results as the goals are not clear.
Asset Register and Preventive Maintenance Plans
Preparing a detailed asset register, listing all the parent and child equipment, and equipment grouping will be a good starting point. OEM specifications and recommended preventive maintenance plans including schedules and task lists can be used as a baseline.
The first step of the Preventive Maintenance program is to prepare the preventive maintenance plans at the equipment level with all the tasks, their desired frequency, estimated time, spare part changes etc. Time-based maintenance can be supplemented with usage-based maintenance plans and condition-based maintenance schedules and job plans.
Comprehensive View and Assessment
Once individual equipment preventive maintenance plans are prepared, they can be reassessed with the plant view. There will be hundreds or thousands of equipment-level preventive maintenance plans and the next task is to do comprehensive planning. In involves
- Evaluating the complete preventive maintenance plans for all the assets together in a given line or section based on dependencies and optimizing the overall program for collective improvement.
- Prioritization ranking can be computed based on equipment criticality, failure history, and operating conditions.
- Differentiating the short-term preventive maintenance (eg. Monthly routine maintenance) from that of long-term preventive maintenance needs (eg. Annual preventive maintenance plan or Shutdown maintenance plan) and planning their schedules and checklists as per the objectives.
- Hybrid preventive maintenance programs that have a suitable mix of time-based, usage-based and condition-based triggers and predictive maintenance aspects can improve the efficiency of Preventive Maintenance programs.
- Planning boards with visuals of equipment calendars, resource allocation, tools reservations, spare requirements and vendor support required can give a total perspective to do necessary resource levelling, scheduling adjustments and spare ordering.
Metrics-based Maintenance
Operational Metrics like Preventive Maintenance Compliance (PM Compliance or PMC), Preventive Maintenance effectiveness (PM Effectiveness), and ageing analysis of overdue tasks can help monitor the status and progress. Accounting metrics like the cost of maintenance, life cycle costs and budget vs actuals can provide more financial insights. Peer class comparison of metrics can give the relative performance of the equipment with reference to its category. Defining and tracking comprehensive metrics management with associated KPI (Key Performance Indicators) dashboards can help institute goal-based maintenance and improve the Preventive Maintenance program efficiency.
Continuous Improvement
Periodic review of the preventive maintenance work orders completed can provide many learnings and insights that can lead to incremental improvements as well as breakthroughs. Best practices include strengthening preventive maintenance schedules and checklists based on root cause analysis of breakdowns, review of maintenance history to avoid overdoing of preventive maintenance, peer class learning and horizontal deployment etc. Standardization of Preventive Maintenance schedules and checklists based on equipment category and training people can help in productivity and efficiency. Continuous improvement reduces waste, increases the quality of maintenance and repairs, people’s productivity and efficiency and can result in a better return on investments.
Preventive Maintenance Software
Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS Systems or CMMS Software) can help in managing all aspects of the Preventive Maintenance Program comprehensively and effectively. CMMS software can cover the entire life cycle of asset management and address the different plant maintenance activities like reactive maintenance, corrective maintenance, preventive maintenance, prescriptive maintenance and predictive maintenance in an integrated way.
CMMS software also has built-in tools to visualize Preventive Maintenance planning boards for all plant assets, standardize schedules and checklists, prioritize and adjust schedules, administer preventive maintenance work orders, track the preventive maintenance work orders completion, monitor overdue tasks and incomplete tasks, measure KPIs and other metrics, display complete equipment history etc.
Building an effective Preventive Maintenance program that consistently delivers business results is a challenge. Breaking it into individual steps and optimizing them one at a time to align with the asset management goals is an easy way to achieve maintenance efficiency. Support systems in terms of technology, systems, processes, metrics and continuous improvement mindset can help in the successful implementation of the Preventive Maintenance Program.
MaintWiz Industry 4.0 CMMS Software helps you build Effective Preventive Maintenance Programs Easily and Efficiently. MaintWiz has rich features and functionalities to optimize the planning and execution of your preventive maintenance programs. MaintWiz Industry 4.0 CMMS Software, has Zero Implementation time and you can set up your preventive maintenance programs on day one.

Jai Balachandran is an industry expert with a proven track record in driving digital transformation and Industry 4.0 technologies. With a rich background in asset management, plant maintenance, connected systems, TPM and reliability initiatives, he brings unparalleled insight and delivery excellence to Plant Operations.
Recent Posts
- From Chaos to Order: Simplifying Maintenance Management with Technology
- From Crisis to Control:Regaining Stability with Effective Breakdown Response
- Avoiding Pitfalls: The 7 Biggest Mistakes Plant Managers Make in Maintenance
- Quality Matters: Improve OEE by Reducing Defects and Rework with MaintWiz CMMS
- How to Implement an Effective Lubrication Program for Your Plant Maintenance Strategy
Recent Comments
Company




